Top-down vs Bottom-up approach in Dynamic Programming
There are two ways to solve and implement dynamic programming problems: 1) Top-down approach and 2) Bottom-up approach. Both approaches are similar in one way: They use extra memory to store the solution to sub-problems to avoid recomputation and improve performance by a huge margin. On another side, both of them are different in so many ways, and understanding this difference would help us to learn dynamic programming from another perspective.
How top-down approach works?
In the top-down approach, we implement the solution naturally using recursion but modify it to save the solution of each subproblem in extra memory. This will first check whether it has previously solved the subproblem. If yes, it returns the stored value and reduce large number of repeated calculations. Otherwise, top-down approach will calculate the sub-problem solution recursively. We say it is the memoized version of a recursive solution, i.e., it remembers what results have been computed previously.
Visualization: Finding the 5th Fibonacci using top-down approach
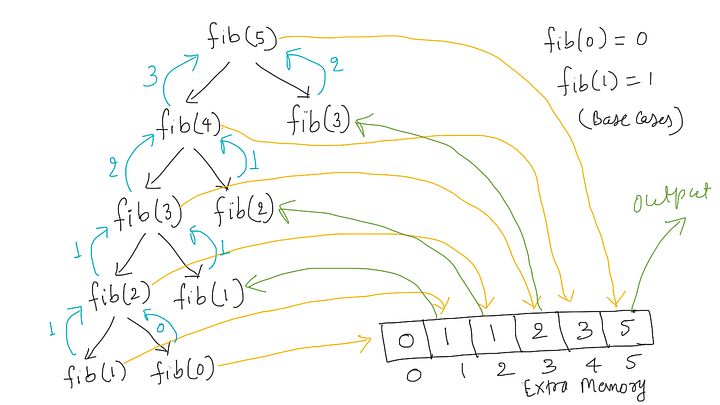
How bottom-up approach works?
On another side, bottom-up approach is just the reverse but an iterative version of the top-down approach. It depends on a natural idea: solution of any subproblem depends only on the solution of smaller subproblems. So bottom-up approach sorts the subproblems by their input size and solves them iteratively in the order of smallest to largest. In other words, before finding the solution of a particular subproblem, bottom-up approach will first solve all the required smaller subproblems and store their values in extra memory.
Visualization: Finding the 5th Fibonacci using bottom-up approach
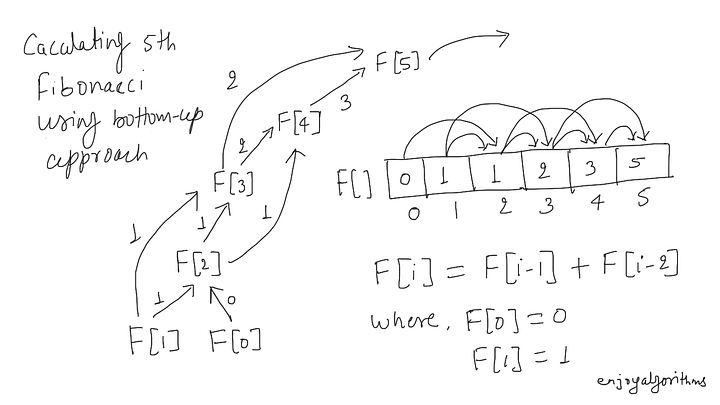
Here are some critical differences
- Top-down is a recursive approach, while bottom-up is an iterative approach. In other words, the top-down approach solve subproblems using the smaller sub-problem only once using the recursion. In reverse, bottom-up build subproblems’ solution iteratively using the smaller sub-problems.
- Most of the time, top-down approach is easy to implement because we just need to modify the recursive solution to add the feature of memoization. In bottom-up approach, we need to define an iterative order to fill the table and take care of several boundary conditions.
- Top-down approach is slower than the bottom-up approach because of the overhead of the recursive calls. In other words, bottom-up approach often has much better constant factors since it has no overhead for recursive calls.
- Top-down approach has also the space overhead of the recursion call stack. If the recursion tree is very deep, we may run out of stack space, which will crash our program.
- Asymptotically, both of these approaches guarantee the same time complexity, except in unusual circumstances where the top-down approach does not actually recurse to examine all possible subproblems.
- Top-down approach starts from the large input size, reaches the smallest version of the problem (base case), and stores subproblem solutions from the base case to the larger problem. In bottom-up approach, we first store the solution for the base case and store subproblem solutions in an iterative order from the base case to the larger sub-problem.
- With the bottom-up approach, sometimes, there is scope to optimize the time and space complexity further. We can try to reduce one loop or try to save space from O(n²) to O(n) or O(n) to O(1). But such types of optimization are challenging to achieve in a top-down approach.
Enjoy learning, Enjoy algorithms!
Share Your Insights
More from EnjoyAlgorithms
Self-paced Courses and Blogs
Coding Interview
OOP Concepts
Our Newsletter
Subscribe to get well designed content on data structure and algorithms, machine learning, system design, object orientd programming and math.
©2023 Code Algorithms Pvt. Ltd.
All rights reserved.
